The State of Climate Change - Today
In an era marked by unprecedented technological advancements, we continue to face the rapidly developing consequences of climate change. Climate.org recently reported that “2023 was the warmest year since global records began in 1850 by a wide margin”, bringing record-breaking heatwaves across the globe. The urgency to address environmental sustainability has never been more pressing.
Amidst this backdrop, the developer community stands at a pivotal juncture. While technology has undoubtedly transformed our lives for the better, it also bears a responsibility to mitigate its environmental footprint and contribute to sustainable practices.
What is Green Coding?
Green Coding is a software engineering practice that aims to reduce the environmental impact of code by reducing its energy consumption. To achieve this, developers must avoid what some people call “Green Code smells”, which are poor design or implementation choices that affect the program's carbon footprint.
This Green Software Foundation article by Olivier Le Goaer, Co-Founder of ecoCode, highlights how green coding is a matter of code quality, emphasizing how static code analysis tools like SonarQube Server help developers detect green code smells in an automated way. And we cannot agree more: green code smells are effectively Clean Code issues!
Green Coding with Clean Code - ecoCode Challenge Paris
At Sonar, we recognize the need to integrate sustainability into the fabric of technological innovation. As a proud sponsor of the ecoCode Challenge Paris, a hackathon for the ecoCode open-source project that aims at reducing the carbon footprint of digital services, we are excited to see how SonarQube Server is empowering developers to prioritize environmental sustainability in their projects.
I had the pleasure of attending this year’s ecoCode Challenge in Paris as a speaker, along with my colleague Geoffray Adde who supported the teams as a coach.
(Pictured: Fabrice Bellingard, VP of Products, presenting: “Open Source: The Engine of Collective Intelligence for a Brighter Future)
Hosted by Groupe Crédit Agricole, 120 developers participated in a 2-day hackathon with the goal of reducing the carbon footprint of digital services through the definition, implementation, and validation of SonarQube Server rules that identify green code smells.
Supported by 30 coaches and 50 partners across 3 challenges (spotters/builders/checkers), the halls were lit up with the shared goal of contributing to and thinking collectively about green coding around the ecoCode solution. What a wonderful endeavor!
After 48 hours of work and thousands of lines of code, the 120 participants were judged on the quality of their renderings, the presentation of their work and also on criteria such as teamwork. Congratulations to the winning teams Nobium, Checker Lithium, Builder Neodymium, and Dashboard Germanium.
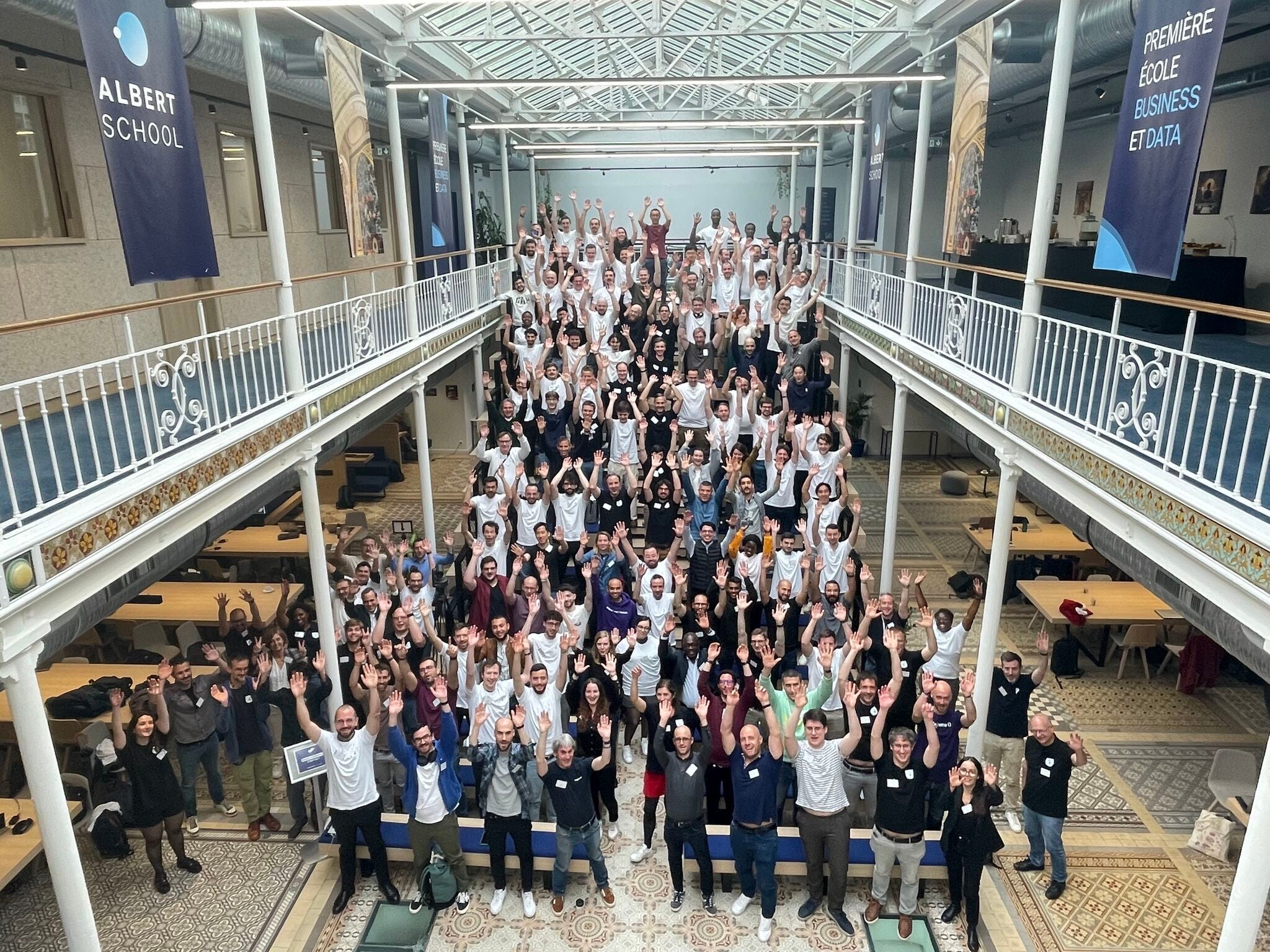

(Pictured: The participants, coaches, and partners that contributed to ecoCod Challenge Paris 2024 )
ecoCode Challenge Paris represents an opportunity to unite innovation and sustainable coding. By leveraging SonarQube Server and fostering collective intelligence, we can drive meaningful progress towards a greener, more sustainable future.
Harnessing Sustainable Code Quality for a Greener Future
Driven by efforts like ecoCode Challenge and our own passionate developers, we’re excited to share that our Clean Code solutions - SonarQube Server, SonarQube for IDE, and SonarQube Cloud - will introduce functionalities that prioritize environmental sustainability in software development.
We’ll share some exciting updates in the near future - Follow us on social media to stay updated!

