Table of contents
What is PL/SQL & How Does it Work?
Key Features of PL/SQL
Setting up PL/SQL Development Environment
Core Concepts: PL/SQL Syntax and Structure
Advanced PL/SQL Programming: Procedures, Functions, and Packages
PL/SQL Common Challenges, Troubleshooting and Resources
Resources for Learning PL/SQL Programming with Sonar
Sonar’s Role in PL/SQL Workflows
PL/SQL Mastery Roadmap
Start your free trial
Verify all code. Find and fix issues faster with SonarQube.
LoslegenPL/SQL (Procedural Language/Structured Query Language) is Oracle’s procedural extension to SQL, designed specifically to combine the power of SQL with the flexibility of procedural programming constructs. PL/SQL enables developers and database administrators to build robust, scalable, and secure applications that interact directly with Oracle Databases. As an integral technology within the Oracle ecosystem, PL/SQL is used for creating scripts, stored procedures, functions, triggers, and packages that facilitate data manipulation and automation.
What is PL/SQL & How Does it Work?
PL/SQL is a block-structured language, meaning programs are organized into logical units called blocks. These blocks can encapsulate declarations, executable statements, and exception handlers, making code modular and maintainable. Blocks are categorized as anonymous blocks, procedures, functions, and triggers.
PL/SQL allows users to define variables, constants, cursors, and control constructs such as loops and conditional statements, providing substantial functionality beyond standard SQL. Its tight integration with Oracle SQL ensures efficient querying, transaction management, and error handling, giving developers granular control over data operations.
Key Features of PL/SQL
PL/SQL stands out among procedural database languages, thanks to a rich feature set designed for robust, organized, and high-performance application development. Here’s an in-depth look at its most critical capabilities:
Exception Handling
Exception handling in PL/SQL allows developers to intercept and manage runtime errors gracefully, avoiding abrupt application termination and improving overall reliability. By defining exception blocks, you can catch standard or custom errors, log them, perform corrective actions, or propagate them to higher levels.
Common exceptions include:
NO_DATA_FOUNDfor missing query resultsTOO_MANY_ROWSwhen a SELECT returns more than expectedDUP_VAL_ON_INDEXfor duplicate index entries
Structured exception handling ensures programs remain stable and user-friendly, even when unexpected situations occur.
Support for Packages
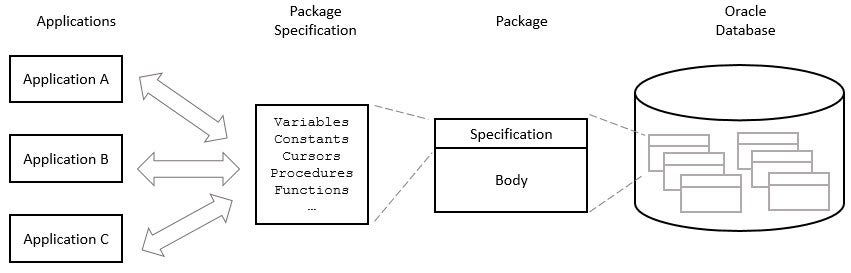
Packages are a modularization feature that let you group logically related procedures, functions, variables, cursors, and exceptions.
Packages are split into:
- Specification: the public interface that declares accessible objects
- Body: the private implementation, encapsulating code and internal workings
This approach:
- Enables code reuse and improved organization
- Facilitates access control—only desired components are exposed
- Improves maintainability by storing related logic together
Cursors
Cursors give you programmatic control over result sets, enabling row-by-row data processing.
Types include:
- Implicit cursors: used automatically by the engine for single-row queries
- Explicit cursors: defined by developers to iterate through multiple rows
Cursors allow retrieval, manipulation, and examination of individual records within a dataset—ideal for complex business logic, data validation, or reporting routines.
Triggers
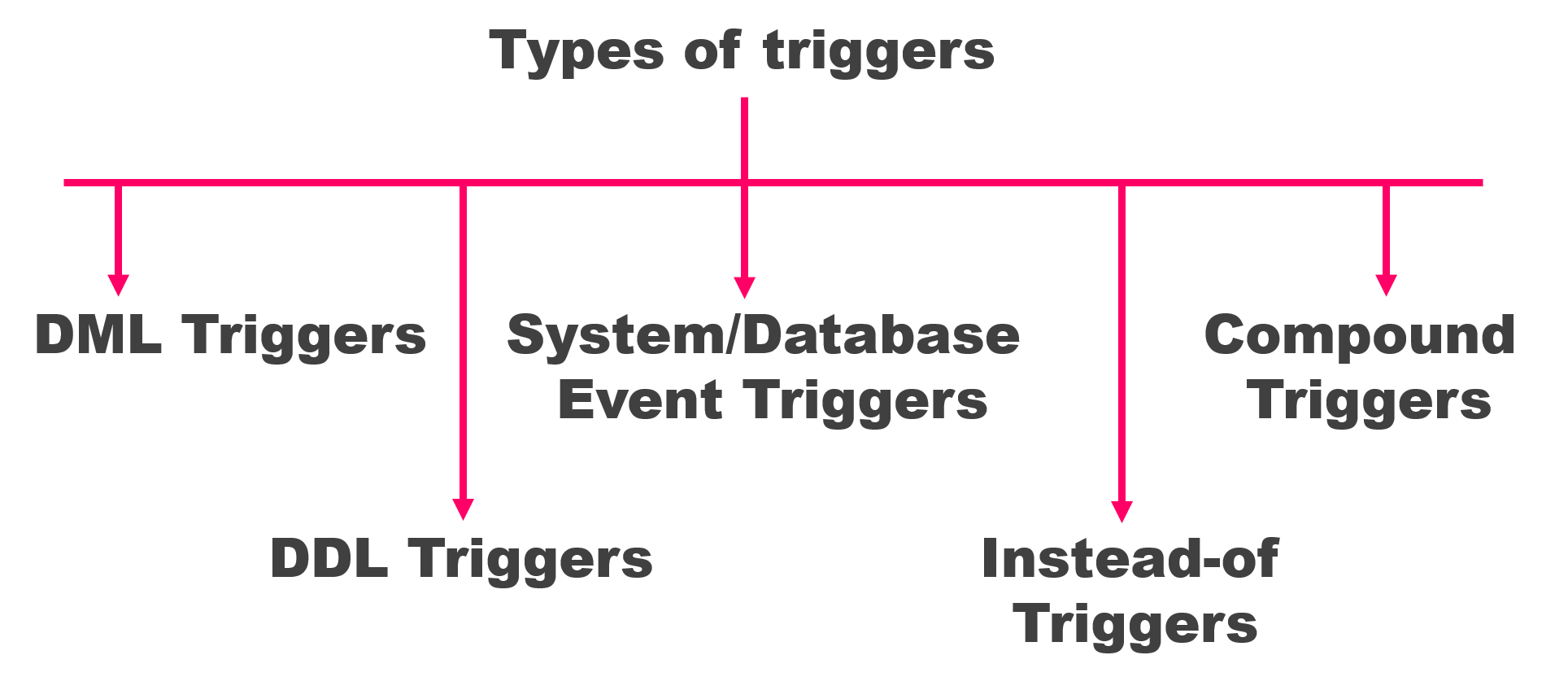
Triggers are PL/SQL blocks that execute automatically in response to specific database events, such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations.
You can create triggers that:
- Enforce data integrity rules
- Log changes for auditing purposes
- Implement custom business logic
- Cascade updates and maintain cross-table consistency
Triggers enhance automation, reliability, and control at the database layer, often freeing applications from redundant logic.
Bulk Processing
Bulk processing commands like BULK COLLECT and FORALL dramatically speed up large-volume data operations.
BULK COLLECTfetches multiple rows into collections in a single stepFORALLexecutes DML statements for all entries in a collection
These features reduce context-switching between SQL and PL/SQL engines, resulting in significant performance improvements for ETL, batch jobs, and mass updates.
Data Security and Privilege Management
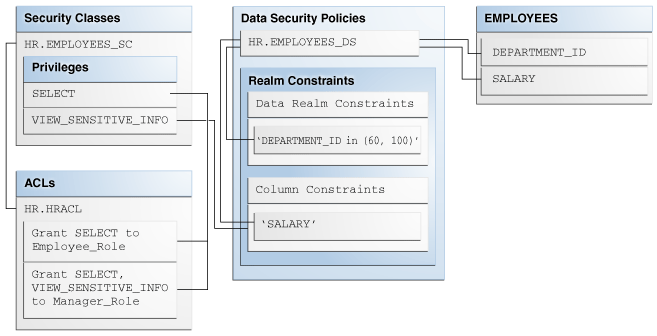
PL/SQL fully leverages Oracle’s security infrastructure, supporting robust authentication, authorization, and privilege control.
- Fine-grained control over access to packages, procedures, and tables
- Integration with roles, schemas, and auditing systems
- Secure handling of sensitive operations
- Developers can enforce data access policies, build audit trails, and comply with regulatory standards, ensuring enterprise-grade protection.
Setting up PL/SQL Development Environment
Configuring Oracle Database for PL/SQL
To start PL/SQL development, an Oracle Database instance is required. Oracle offers various editions such as Oracle Express Edition (XE), Standard, and Enterprise Edition. Installation guides and setup tutorials abound online, with “Oracle PL/SQL setup,” “PL/SQL developer tools,” and “Oracle SQLPlus” being common search terms. Developers use tools like Oracle SQL Developer, TOAD, or command-line interfaces (SQLPlus) to write and execute PL/SQL code.
Recommended Tools and IDEs
Oracle SQL Developer is a powerful, free IDE tailored for PL/SQL development, providing features like schema browsing, debugging, and code formatting. TOAD, DBeaver, and other third-party tools further streamline coding, testing, and deploying PL/SQL routines. Setting up these tools correctly boosts productivity, code quality, and maintainability.
Core Concepts: PL/SQL Syntax and Structure
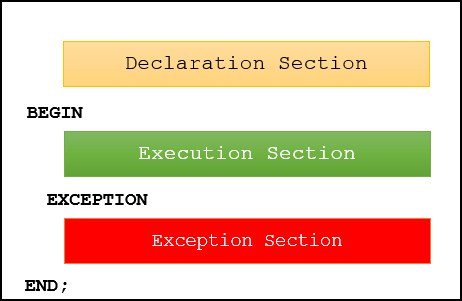
PL/SQL Block Anatomy
Each PL/SQL block consists of three sections: DECLARE, BEGIN, and EXCEPTION. The DECLARE section is optional and used for declaring variables, constants, cursors, and types. The BEGIN section contains executable code, while the EXCEPTION section handles runtime errors, ensuring robust fault tolerance.
Variables and Data Types
PL/SQL supports a wide array of data types, including scalar types (NUMBER, VARCHAR2, DATE), composite types (RECORD, TABLE), and reference types (REF CURSOR). Declaring variables efficiently enables accurate data manipulation and minimizes resource waste.
Using descriptive variable names and leveraging the %TYPE and %ROWTYPE attributes increases maintainability, helps prevent errors, and supports semantic clarity—reflecting best practices highlighted in highly ranked resources.
Advanced PL/SQL Programming: Procedures, Functions, and Packages
Stored Procedures
A procedure in PL/SQL is a reusable set of statements that perform specific tasks. Procedures can accept parameters, execute SQL queries, handle exceptions, and return output via OUT parameters.
Functions
PL/SQL functions differ from procedures in that they return a single value and can be used in SQL expressions. Functions support validation, calculation, and transformation of data.
Packages
Packages group logically related procedures, functions, and variables. They provide encapsulation, public/private visibility, and improved manageability.
Common PL/SQL Use Cases and Real-World Examples
PL/SQL is a versatile technology that underpins essential operations across industries—including banking, ERP, CRM, e-commerce, and data warehousing—where accuracy, security, and automation are paramount.
- Automates transaction processing, reconciliation, and fraud detection in banking systems for reliable financial operations.
- Manages billing, data validation, and integration within ERP platforms to streamline enterprise workflows.
- Drives business logic and customer data management for CRM applications, enhancing user engagement and sales efficiency.
- Supports order processing, inventory control, and returns management in e-commerce environments for seamless customer experiences.
- Enables batch reporting, ETL, and auditing in data warehouses, helping organizations achieve actionable insights and regulatory compliance.
By leveraging robust PL/SQL routines, organizations benefit from increased reliability, enhanced security, and scalable application performance.
PL/SQL Common Challenges, Troubleshooting and Resources
PL/SQL development comes with its own set of challenges, but proven troubleshooting strategies and community resources help developers resolve issues and maintain high-quality code.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Inefficient SQL queries, unnecessary context switching between PL/SQL and SQL, and lack of bulk processing can slow down routines. Profiling tools like Oracle’s SQL Trace, TKPROF, and Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) help identify slow queries, resource-heavy operations, and optimize execution plans for better performance.
- Memory Leaks: Poor management of large collections, cursors, and temporary tables may lead to excessive memory usage. Developers should always close unnecessary cursors, avoid storing large result sets in memory, and leverage bulk operations carefully. Monitoring scripts and memory profiling utilities within the Oracle ecosystem help track and resolve leaks.
- Complex Debugging: Troubleshooting multi-layered logic and diagnosing unexpected behavior can be challenging in PL/SQL. Tools like Oracle SQL Developer’s debugger, logging packages, and systematic use of exception handling and meaningful error messages make it easier to track down problems.
- Version Incompatibilities: Migrating code between different Oracle versions or adapting to platform upgrades may introduce compatibility issues. Consulting Oracle’s official migration guides and release notes, using code analysis tools, and testing in isolated environments help minimize downtime and prevent errors.
- Community Support and Resources: Oracle’s extensive documentation, as well as active PL/SQL forums (such as Oracle Community, Stack Overflow, and specialized blogs), offer quick access to expert advice and practical tips. Peer-driven Q&A, real-world examples, and open-source code repositories accelerate problem resolution and knowledge growth.
With the right combination of diagnostic tools, strategic troubleshooting, and community engagement, developers can efficiently overcome PL/SQL challenges and maintain robust, scalable applications.
Resources for Learning PL/SQL Programming with Sonar
For developers looking to master PL/SQL and elevate code quality, Sonar provides a suite of resources tailored for every stage of the PL/SQL coding journey.
- PL/SQL Language-Specific Documentation:
Kick off your journey with Sonar’s dedicated PL/SQL page which offers in-depth guides for setting up, integrating, and analyzing PL/SQL projects using SonarQube. These resources help developers understand core static analysis features, apply coding standards, and leverage tools for automatic code review and instant quick fixes—ensuring your PL/SQL code is secure, reliable, and maintainable. - Multi-Language Resource Hub:
Broaden your perspective by exploring Sonar’s multi-language resource hub. Here, you’ll see how PL/SQL fits alongside the many languages and frameworks Sonar supports. This hub enables comparison of best practices and static analysis capabilities across technologies, helping you reinforce good habits as you switch between programming languages. - Sonar Blog:
Stay updated with the latest PL/SQL programming insights, troubleshooting strategies, and real-world coding examples on the regularly updated Sonar blog. This platform features articles on improving PL/SQL code robustness, tips for optimizing performance, and deep dives into both foundational and advanced topics.
Sonar’s Role in PL/SQL Workflows
Sonar plays a pivotal role in enhancing PL/SQL workflows by providing advanced code quality and security analysis tailored for Oracle database development. By integrating seamlessly with existing development pipelines, Sonar enables teams to automatically scan PL/SQL scripts, stored procedures, packages, and triggers for vulnerabilities, code smells, and compliance issues. This proactive approach ensures that high standards for reliability, maintainability, and performance are maintained—helping organizations rapidly detect problematic patterns and enforce best coding practices before deployment.
With Sonar’s detailed dashboards and actionable reporting, PL/SQL developers gain visibility into code health across projects and releases. Teams can track technical debt, monitor code coverage, and prioritize remediation based on business risk and quality gates. Sonar’s support for collaborative workflows means issues can be assigned, discussed, and resolved efficiently, fostering a culture of continuous improvement within PL/SQL teams. Ultimately, leveraging Sonar in PL/SQL environments leads to more secure, robust database solutions that are easier to evolve and maintain over time.
PL/SQL Mastery Roadmap
Achieving PL/SQL mastery requires a blend of theoretical understanding and extensive real-world experience. Developers should focus on building a strong foundation in PL/SQL syntax, core concepts, and the language's block structure. Applying this knowledge to complex business scenarios—such as transaction management, batch processing, and multi-step validation—helps hone practical skills. Regularly working with advanced constructs like cursors, exception handling, packages, and triggers, as well as performance-enhancing features such as bulk operations and optimization techniques, enables professionals to create more efficient and maintainable solutions. Embracing best practices, including rigorous code reviews, clear documentation, and structured error handling, ensures work remains robust and reliable as application complexity grows.
Staying at the forefront of PL/SQL development also means keeping pace with Oracle’s latest features and industry standards. Active engagement in online communities and forums—such as Oracle’s official channels, Stack Overflow, and technical blogs—allows developers to learn from shared experiences and troubleshoot new challenges collaboratively. Consulting comprehensive guides, documentation, and following thought leaders further deepens understanding, while participation in webinars and training enhances hands-on learning. This commitment to ongoing education and peer exchange not only strengthens technical expertise but also builds the professional reputation and authority necessary for a PL/SQL specialist in today’s fast-evolving enterprise environments.
