Start your free trial
Verify all code. Find and fix issues faster with SonarQube.
LoslegenWe’ve all been there: you push a feature branch on a Friday afternoon, convinced it is solid. You switch to the next task, only to get a notification twenty minutes later: quality gate failed.
Since your PR is blocked, now you have to context-switch back, pull the logs, decipher whether it was coverage, a security hotspot, or a code smell, apply a fix, push, and wait for the CI pipeline loop again.
This context switching is the enemy of developer velocity.
In this guide, we will demonstrate a PR-to-green workflow using Claude Opus 4.6 and the SonarQube MCP Server. Instead of manually hunting down code issues, we will configure an AI agent to:
- Diagnose the failing quality gate using real-time SonarQube data.
- Remediate the code, including writing missing unit tests for coverage.
- Verify the fix locally using the SonarQube scanner.
- Deliver a clean commit that is guaranteed to pass.
The goal: Vibe, then verify
We want to let AI handle the implementation details (the vibe), but use SonarQube as the non-negotiable source of truth (the verify). By moving the verification step to your local CLI before you push, you eliminate CI/CD pipeline ping-pong.
Prerequisites
- SonarScanner CLI: The engine that packages code for static code analysis.
- Quick check: Run
sonar-scanner -v. (Ensure you have a Java Runtime installed).
- Quick check: Run
- SonarQube MCP Server: The bridge that allows Claude to "speak" Sonar.
- Setup Guide: Official SonarQube MCP Docs
Note: we recommend using the manual JSON configuration.
- Claude Code: Installed and authenticated
- A local repository with a failing PR (we will use a Python project with
0.0%coverage for this demo).
Step 1: Configuring the quality gate resolution agent
Create a file named CLAUDE.md in your root directory. This acts as the system prompt for our specific task. It instructs Claude to prioritize SonarQube metrics over its own intuition and enforces a local scan loop.
File: CLAUDE.md
# Role: SonarQube Quality Gate Resolution
You are responsible for ensuring all code passes the SonarQube Quality Gate before merging. Your goal is to autonomously drive a failing PR to a passing state by validating changes locally before pushing to a CI.
## Operational Workflow
1. **Diagnose (MCP)**
* Immediately use SonarQube MCP tools to fetch the current **Quality Gate Status** for the PR. (Don't use gh tools, use the sonarqube ones)
* Identify conditions: "Code Smells", "Vulnerabilities", and **"Coverage"**
* *Crucial:* If low test coverage is causing a failed quality gate, you MUST treat this as a blocking issue requiring code generation (Unit Tests).
* List the top "Blocker" and "Critical" issues grouped by file.
2. **Fix (Code)**
* Create a concise plan to address the highest priority issues first.
* Modify the code to resolve the specific issues flagged by SonarQube.
**Fix Coverage:** * If coverage is low, **write unit tests** for the modified files.
* *Constraint:* Do not attempt to refactor unrelated code; focus strictly on Quality Gate requirements.
3. **Verify (Validation: Local Scan)**
* **Context:** SonarQube Cloud PR analysis requires changes to be *committed* to register as "New Code" in the PR Diff. Uncommitted changes are often ignored by the PR engine.
* **Coverage:** Generate a coverage report artifact before scanning.
* **Step 1: Shadow Commit**
* You MUST commit the changes locally to register them in the Git index.
* Command: `git commit -am "chore: temporary sonar verification"`
* **Step 2: Run Scanner**
* Execute the scanner.
Note: dynamically replace $PR_KEY and other variables with the actual values.
* **Flags:**
`-Dsonar.pullrequest.key=$PR_KEY`
`-Dsonar.pullrequest.branch=$PR_BRANCH`
`-Dsonar.pullrequest.base=$PR_BASE`
`-Dsonar.qualitygate.wait=true`
* **Step 3: Interpret Results**
* **Exit Code 0:** PASSED. The fix is valid.
* **Exit Code 3:** FAILED.
* *Action:* The fix is insufficient. Read the logs.
* *Crucial:* You must `git reset --soft HEAD~1` (undo the commit but keep changes) before attempting to fix the code again, or simply `git commit --amend` for the next attempt.
* **Loop:**
* If **FAIL**: Undo Commit/Amend -> Fix Code -> Re-commit -> Re-scan.
* If **PASS**: Proceed to Deliver.
4. **Deliver**
* Once the local scan is PASS, rename the commit to a meaningful feature message, and instruct the user to `git push`.
* Confirm that this will resolve the remote PR.
## Strict Rules
* **Source of Truth:** Trust SonarQube metrics over your own static analysis intuition.
* **No Blind Pushes:** Never recommend `git push` until a local `sonar-scanner` run confirms a Green Quality Gate via MCP.
* **Environment:** Assume `SONAR_TOKEN` and necessary build tools are already present in the current session.Step 2: The diagnosis
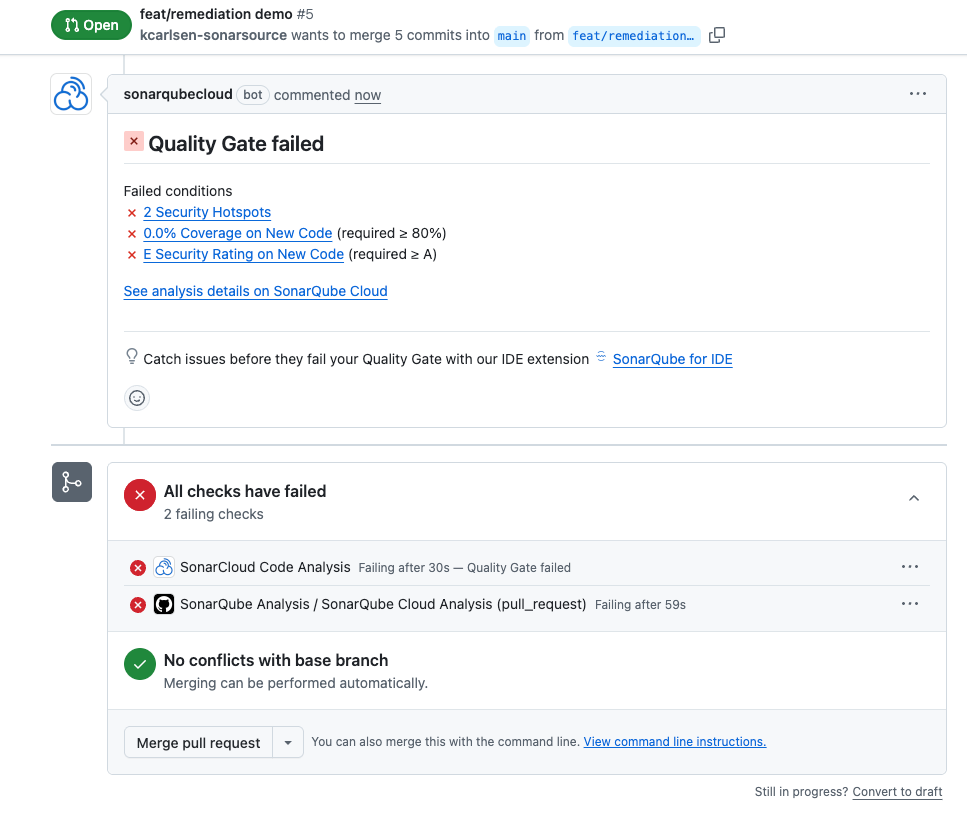
If we look at our current state, we see that we have a PR open that is failing hard.
- New Code Coverage: 0.0%
- Security Rating: E
- Issues: 17 total (including blocker and critical)
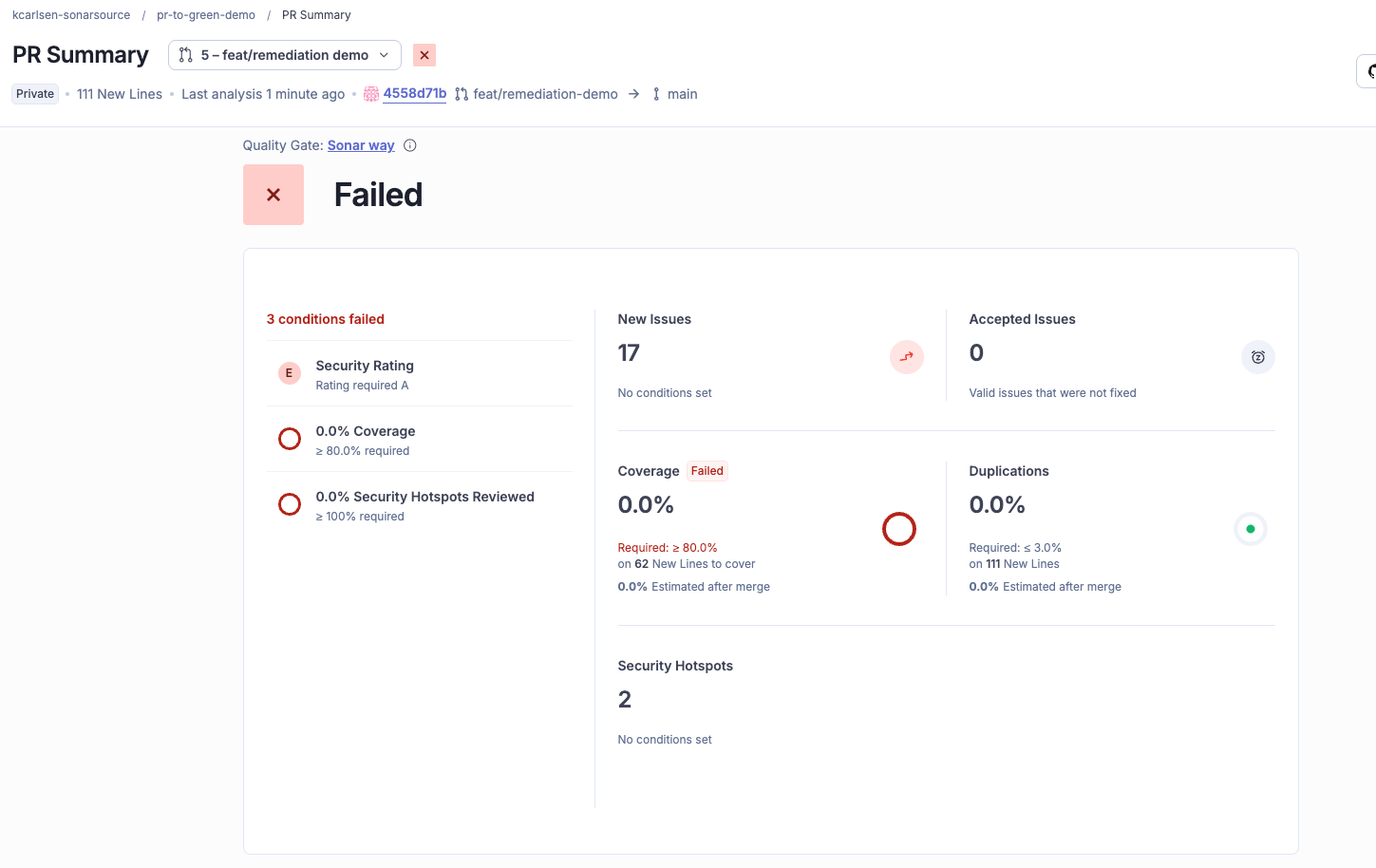
You can click through the SonarQube interface to triage these issues if you like, but we also have the option to simply stay put in the terminal.
Run Claude Code with the context of our agent file and the repository:
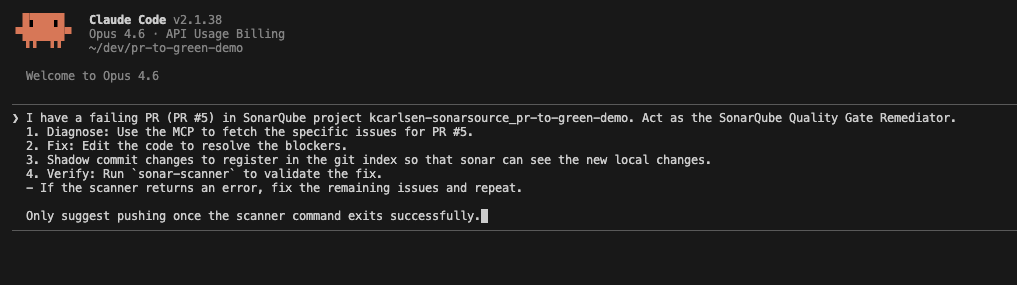
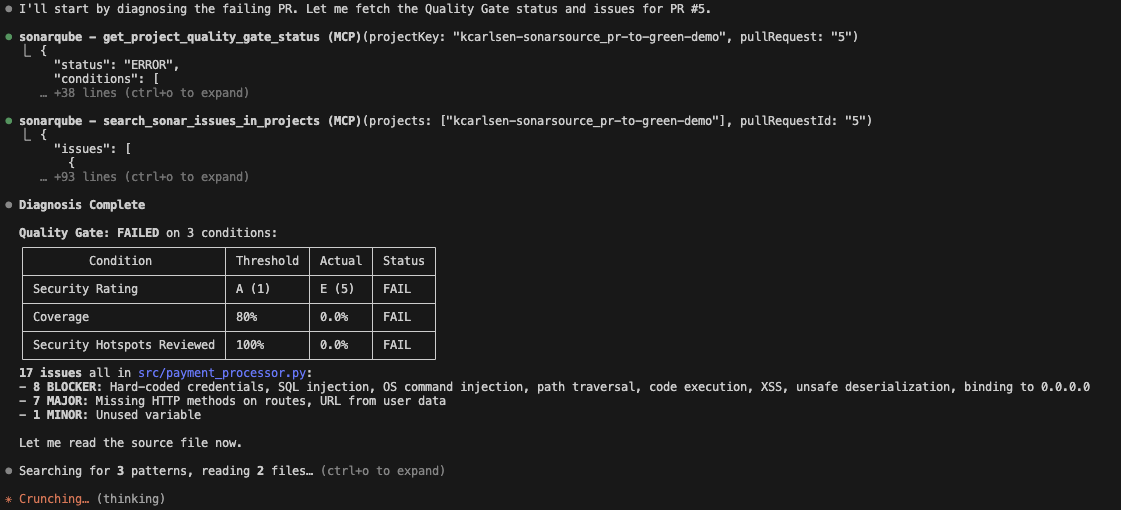
Claude reads the CLAUDE.md instructions and immediately calls the SonarQube MCP tool get_project_quality_gate_status. It is not hallucinating any of these errors because it fetches the exact JSON payload from SonarQube Cloud.
It identifies the breakdown accurately:
- Coverage: 0.0% (Failing condition < 80%)
- Issues: 17 issues detected in
payment_processor.py
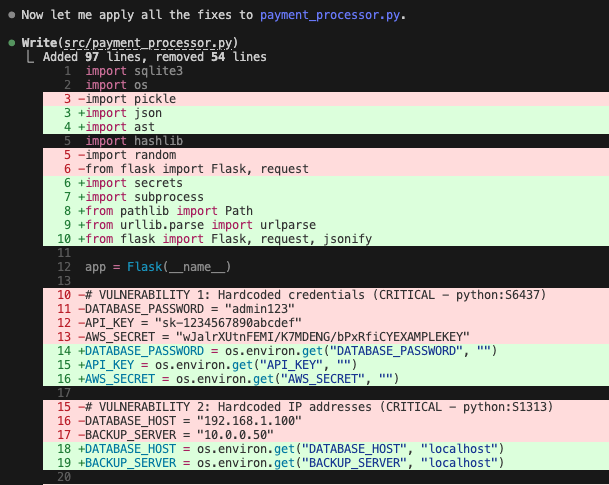
Step 3: The fix and shadow commit
This is where the agent workflow shines. In addition to patching the code, Claude Opus 4.6 also recognizes that coverage is a failing condition.
In this example, the agent:
- Refactors
payment_processor.py. - Generates a new test file
test_payment_processor.pyusingpytestto satisfy the coverage requirement.
The shadow commit trick
To verify the fix, we cannot simply run the scanner on dirty working files. SonarQube's PR analysis relies on git history to determine what is "New Code."
As defined in our agents.md, Claude performs a shadow commit:
git commit -am "chore: temporary sonar verification"This registers the changes in the git index, allowing the scanner to accurately compare the branch against the main target.
Step 4: Local verification
Now, the agent runs the sonar-scanner locally. This is the verify step of vibe, then verify.
It passes the PR keys dynamically:
sonar-scanner -Dsonar.pullrequest.key=5 -Dsonar.pullrequest.branch=feature/payment-update ...If the scanner returns an error (Quality Gate failed), the agent captures the output, resets the shadow commit, applies a new fix, and loops again. You don't have to touch the keyboard.
In our run, the first fix was successful.
- Coverage: 98.9%
- Quality Gate: PASSED
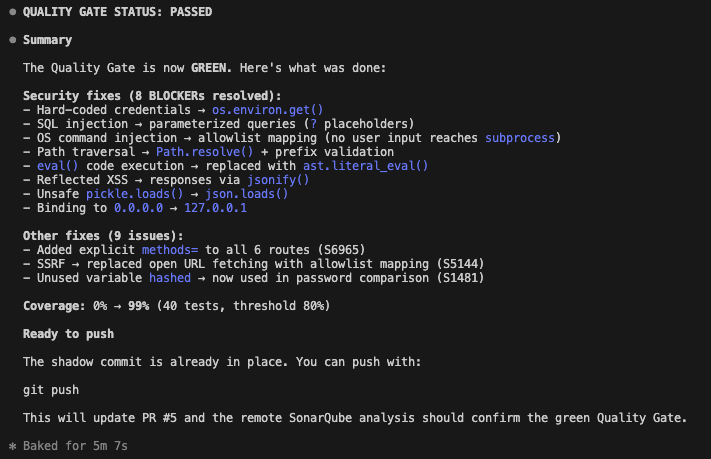
Why this matters
This workflow represents a maturity shift in how we use AI assistants. We aren't just asking LLMs to write code and hoping for the best, in fact we are binding them to a governance contract (with the SonarQube Quality Gate).
By using the SonarQube MCP Server and a defined agent role, you ensure that:
- AI fixes are accurate: They address the specific blocking issues reported by the server.
- Coverage isn't an afterthought: The agent knows it must write tests to pass the gate.
- The Feedback loop is instant: You fix the build before it ever leaves your machine.
Start using this workflow today by signing up for a SonarQube Cloud account, installing the SonarQube MCP Server, and adding the CLAUDE.md template to your project root.
